The slide rule side of the E6B computer is used to calculate time, speed and distance. The scales on the outer circle and the first scale on the inner disk are identical. Also on the inner disk is an additional scale that represents hours corresponding to the number of minutes on the first scale. Think of the edge of the inner disk as representing the word "per", such as "miles per hour", gallons per minute, etc.
To calculate any rate, simply place the black triangle on the inner disk opposite the number on the outer scale that represents the value that changes with time, such as miles per hour and gallons per hour. Then, opposite the number of minutes on the inner disk, you can read the result. Naturally, you need to provide the zero or decimal point if appropriate by first estimating an answer to comply with the TLAR (That Looks About Right) rule.
To compute True Air Speed, use the small window and align the temperature opposite the altitude and read the True Air Speed on the outer scale opposite the Calibrated Air Speed on the inner disk.
Paul Strickland entered the Air Force in 1983, graduating with honors from OCS. Paul has had a distinguished and successful Air Force career logging over 3,900 hours in military aircraft including the A-10, F-5 and F-16. Paul served with various squadrons in the US, Europe, and Korea, flying combat missions during Operation Deny Flight over Bosnia, Operation Northern Watch over Iraq, and supporting Operation ALLIED FORCE over Kosovo as operations director, Combined Air Ops Center in Italy. In 1991, “Sticky” was named to the USAF Air Demonstration Squadron “Thunderbirds” as the #4, Slot pilot, Instructor Pilot, Flight Examiner, and Safety officer. While with the Thunderbirds, he logged over 160+ air shows throughout the United States and two overseas tours, flying in 11 European countries (and the first ever USAF demonstration in Hungary and Poland), and seven South American countries. “Sticky” commanded the 4th Fighter Squadron “Fuujins”, the 388 Ops Support Squadron “Raptors”, and the 8th Ops Group “Wolfpack” at Kunsan, Korea before serving with the Joint Staff, Pentagon as the Chief, Joint Operations Division, SOUTHCOM, until his retirement in 2006. “Sticky” is currently a pilot with Southwest Airlines.
The last combat mission of World War II began Aug. 15, 1945, when fighter pilot Jerry Yellin and his wingman, 19-year-old Philip Schlamberg, took off from Iwo Jima to attack airfields near Nagoya, Japan.
The war seemed all but over. Germany had surrendered in May, and much of Hiroshima and Nagasaki were in ruins, decimated by atomic bombs dropped the previous week. If Mr. Yellin heard a code word — “Utah” — Japan’s rumored surrender had occurred, and he was to cancel his mission and return to Iwo Jima, a rocky island that he had helped secure months earlier and that offered a base for American bombers headed north to Japan.
Later that day, on what was still Aug. 14 in the United States, Emperor Hirohito announced Japan’s surrender. For some reason, however, Mr. Yellin and Schlamberg never got the message.
Taking on antiaircraft fire in their P-51 Mustangs, they strafed their targets and headed home, passing through a thick bank of clouds. Schlamberg, who had previously admitted a sense of foreboding to Mr. Yellin, saying, “If we go on this mission, I’m not coming back,” never emerged from the haze.
Disappearing from Mr. Yellin’s wing, he was presumed dead and considered one of the last Americans to be killed in combat during World War II.

Mr. Yellin in 2015. (Lightfinder Public Relations)
Mr. Yellin, who landed on Iwo Jima to discover that the war had ended three hours earlier, and who later became an outspoken advocate of veterans with post-traumatic stress disorder, died Dec. 21 at his son Steven Yellin’s home in Orlando. He was 93 and had lung cancer, his son said.
For Mr. Yellin, the war was a hellish necessity, essential for halting the spread of Nazism and Japanese aggression. But he also spoke forthrightly about its costs, including the mental anguish over memories of combat that nearly led him to suicide. He recalled with particular horror the experience of landing on war-torn Iwo Jima for the first time, where “there wasn’t a blade of grass and there were 28,000 bodies rotting in the sun.”
“The sights and the sounds and the smells of dead bodies and the sights of Japanese being bulldozed into mass graves absolutely never went away,” he told the Washington Times in August.
Mr. Yellin, a captain in the 78th Fighter Squadron of the Army Air Forces, counted 16 downed pilots in his unit during the war, including Schlamberg. For years afterward, he struggled to keep a steady job, moving a dozen times in the United States and Israel (where he settled, at one point, partly in protest of the Vietnam War).
He eventually found solace through Transcendental Meditation, a twice-daily technique of silent concentration that his wife introduced him to in 1975 after she saw the practice’s originator, Maharishi Mahesh Yogi, on “The Merv Griffin Show.”
Mr. Yellin soon began speaking to other veterans who struggled to adapt to civilian life, and in 2010 he co-founded Operation Warrior Wellness, a division of the David Lynch Foundation that helps veterans learn Transcendental Meditation. He said he was inspired to start the group after a friend and Army veteran killed himself that year. Mr. Yellin received support in promotional videos by actress Scarlett Johansson, a grandniece of Schlamberg.
“The feeling that one has when a buddy dies? You just can’t emulate that. We have a burden civilians will never understand,” Mr. Yellin told The Washington Post earlier this month, shortly after the release of “The Last Fighter Pilot,” an account of his World War II service written with Don Brown.
The great thing about the mechanical E6B computer is that it requires no batteries and gets more accurate the more often you use it! The easy way to use the wind side of the E6B is remember to start with placing the wind direction under the True Index. Align the grommet over any solid line on the slide, and draw a wind dot UP a distance representing the wind speed.
Next, rotate the bezel to place the true course under the True Index. Now, move the slide until the wind dot is over the line that represents the true airspeed.
Finally, without moving anything, read your groundspeed under the grommet and read your wind correction angle under the near-vertical line that radiates from the bottom of the slide.
From Brian Schiff's website:
Capt. Brian Schiff is a captain for a major US airline and is type-rated on the Boeing 727, 757, 767, DC-9 (MD-80), CL-65, LR-JET, and G-V. Schiff’s roots are deeply planted in general aviation where he has flown a wide variety of aircraft.
He holds several flight instructor ratings and is recognized for his enthusiasm and ability to teach in way that simplifies complex procedures and concepts. He has been actively instructing since earning his flight and ground instructor certificates in 1985. Schiff also has been an FAA-designated examiner.
He attended San Jose State University, and earned his Bachelor of Science degree in Aeronautical Science from Embry-Riddle Aeronautical University and his Masters of Science Degree in Aviation Safety from the University of Central Missouri. He regularly conducts seminars about aviation safety and techniques to student and professional pilots alike.
Here's a great website that features a visit with Brian: http://karlenepetitt.blogspot.com/2017/11/brain-schiff.html
Brian's website has tons of great information for pilots at every level of experience.
IMSAFE is the Aeronautical Information Manual's recommended mnemonic for aircraft pilots to use to assess their fitness to fly.
The mnemonic is:
- Illness - Is the pilot suffering from any illness or symptom of an illness which might affect them in flight?
- Medication - Is the pilot currently taking any drugs (prescription or over-the-counter)?
- Stress - Is the pilot overly worried about other factors in his life? The psychological pressures of everyday living can be a powerful distraction and consequently affect a pilot's performance.
- The Yerkes-Dodson study illustrates that performance actually improves with increasing levels of stress up to a certain level, then drops off rapidly if the stress level is too great.
- Alcohol - Although legal limits vary by jurisdiction (0.04 BAC, any consumption in the past 8 hours or current impairment in the USA), the pilot should consider their alcohol consumption within the last 8 to 24 hours.
- Fatigue - Has the pilot had sufficient sleep and adequate nutrition?
- Emotion - Has the pilot fully recovered from any extremely upsetting events such as the loss of a family member?
'E', while defined under the FAA as standing for Emotion, is considered by other international Aviation Authorities such as the CAA and CASA to stand for Eating, including ensuring proper hydration, sustenance, and correct nutrition.
Dean Siracusa used to fly in his father's airplane as a child, but when he started traveling by air as an adult he developed a fear of flying. To combat this fear, he started taking flying lessons in 1999, and immediately fell in love with aviation.
Dean has owned a Cessna 172, a Grumman Cheeta, and his current airplane, a Myers 200D. He's put 1000 hours on the Myers since buying it in 2006, and still raves about the plane.
In 2010 Dean noticed a major problem with aviation sunglasses: the temple pieces dig into the wearer's head when using a tight-fitting headset or helmet. That started him on his quest to design and develop sunglasses with micro-thin temples that are comfortable under the headgear worn for any activity, such as flying, cycling, and skiing. The result was a ground-breaking line of eyewear designed for aviation, and currently in use by pilots of C-130s, F-16s and a host of other military and civilian airplanes.
Glasses can be ordered directly from his website and also at numerous optical retailers.
It is estimated that once fully adapted to darkness, the rods are 10,000 times more sensitive to light than the cones, making them the primary receptors for night vision. Since the cones are concentrated near the fovea, the rods are also responsible for much of the peripheral vision. The concentration of cones in the fovea can make a night blindspot in the center of the field of vision.To see an object clearly at night, the pilot must expose the rods to the image.This can be done by looking 5° to10° off center of the object to be seen.This can be tried in a dim light in a darkened room. When looking directly at the light, it dims or disappears altogether. When looking slightly off center, it becomes clearer and brighter.
When looking directly at an object, the image is focused mainly on the fovea, where detail is best seen. At night, the ability to see an object in the center of the visual field is reduced as the cones lose much of their sensitivity and the rods become more sensitive. Looking off center can help compensate for this night blind spot. Along with the loss of sharpness (acuity) and color at night, depth perception and judgment of size may be lost.
Dark Adaptation
Dark adaptation is the adjustment of the human eye to a dark environment. That adjustment takes longer depending on the amount of light in the environment that a person has just left. Moving from a bright room into a dark one takes longer than moving from a dim room and going into a dark one.
While the cones adapt rapidly to changes in light intensities, the rods take much longer. Walking from bright sunlight into a dark movie theater is an example of this dark adaptation period experience. The rods can take approximately 30 minutes to fully adapt to darkness. A bright light, however, can completely destroy night adaptation, leaving night vision severely compromised while the adaptation process is repeated.
Scanning techniques are very important in identifying objects at night. To scan effectively, pilots must look from right to left or left to right. They should begin scanning at the greatest distance an object can be perceived (top) and move inward toward the position of the aircraft (bottom). For each stop, an area approximately 30° wide should be scanned. The duration of each stop is based on the degree of detail that is required, but no stop should last longer than 2 to 3 seconds. When moving from one viewing point to the next, pilots should overlap the previous field of view by 10°.
Off-center viewing is another type of scan that pilots can use during night flying. It is a technique that requires an object be viewed by looking 10° above, below, or to either side of the object. In this manner, the peripheral vision can maintain contact with an object.
With off-center vision, the images of an object viewed longer than 2 to 3 seconds will disappear. This occurs because the rods reach a photochemical equilibrium that prevents any further response until the scene changes. This produces a potentially unsafe operating condition. To overcome this night vision limitation, pilots must be aware of the phenomenon and avoid viewing an object for longer than 2 or 3 seconds. The peripheral field of vision will continue to pick up the object when the eyes are shifted from one off- center point to another.
Several things can be done to help with the dark adaptation process and to keep the eyes adapted to darkness. Some of the steps pilots and flight crews can take to protect their night vision are described in the following paragraphs.
If, during the flight ,any high intensity lighting areas are encountered, attempt to turn the aircraft away and fly in the periphery of the lighted area.This will not expose the eyes to such a large amount of light all at once. If possible, plan your route to avoid direct over flight to built-up, brightly lit areas.
Flight deck lighting should be kept as low as possible so that the light does not monopolize night vision. After reaching the desired flight altitude, pilots should allow time to adjust to the flight conditions.This includes readjustment of instrument lights and orientation to outside references. During the adjustment period, night vision should continue to improve until optimum night adaptation is achieved. When it is necessary to read maps, charts, and checklists, use a dim white light flashlight and avoid shining it in your or any other crew member’s eyes.
Often time, pilots have no say in how airfield operations are handled, but listed below are some precautions that can be taken to make night flying safer and help protect night vision.
•Airfield lighting should be reduced to the lowest usable intensity.
•Maintenance personnel should practice light discipline with headlights and flashlights.
•Position the aircraft at a part of the airfield where the least amount of lighting exists.
If a night flight is scheduled, pilots and crewmembers should wear neutral density (N-15) sunglasses or equivalent filter lenses when exposed to bright sunlight. This precaution increases the rate of dark adaptation at night and improves night visual sensitivity.
Unaided night vision depends on optimum function and sensitivity oftherods of the retina. Lack of oxygen to the rods (hypoxia) significantly reduces their sensitivity. Sharp clear vision(with the best being equal to 20–20 vision) requires significant oxygen especially at night. Without supplemental oxygen, an individual’s night vision declines measurably at pressure altitudes above 4,000 feet. As altitude increases, the available oxygen decreases, degrading night vision. Compounding the problem is fatigue, which minimizes physiological well being. Adding fatigue to high altitude exposure is a recipe for disaster. In fact, if flying at night at an altitude of 12,000 feet, the pilot may actually see elements of his orher normal vision missing or not in focus. Missing visual elements resemble the missing pixels in a digital image while unfocused vision is washed out.
For the pilot suffering the effects of hypoxia, a simple descent to a lower altitude may not be sufficient to reestablish vision. For example, a climb from 8,000 feet to 12,000 feet for 30 minutes does not mean a descent to 8,000 feet will rectify the problem. Visual acuity may not be regained for over an hour. Thus, it is important to remember, altitude and fatigue have a profound effect on a pilot’s ability to see.
•Select approach and departure routes that avoid highways and residential areas where illumination can impair night vision.
Night flight can be more fatiguing and stressful than day flight, and many self-imposed stressors can limit night vision. Pilots can control this type of stress by knowing the factors that can cause self-imposed stressors.
When John Fairfield visited an Air Force recruiter, he became convinced he should be a navigator to gain additional aviation education before becoming a pilot. He attended navigator training and served as a B-52 Navigator, eventually becoming a check airman and a Navigator-Bombadier. Due to his exceptional performance and attitude, he was selected to attend Air Force Undergraduate Pilot Training as the only Navigator released from Strategic Air Command for this school.
He performed extremely well in pilot training, and had his choice of assignments. He elected to remain in Air Training Command as an Instructor Pilot, to gain additional flight experience. At Williams Air Force Base he became the base expert in T-37 spin recovery training, administering this training to students and instructors alike. After gaining additional flying experience, John volunteered for combat duty in Vietnam.
Following F-4 Replacement Training Unit training, he arrived at the 8th Tactical Fighter Wing, at Ubon Royal Thai Air Base, just as Operation Linebacker commenced. He quickly became a flight commander and flight leader on missions over Hanoi, at the time the most heavily-defended area in the world. He led combat flights during both Linebacker I and Linebacker II.
After Ubon, John was assigned to the Pentagon to manage the Air Force fuel program. A few months after assuming that position, the 1973 Fuel Crisis occurred, and it was his job to ensure that the Air Force could continue flying with drastically reduced fuel stores. Because of his performance in this position, he was promoted from Captain to Colonel in four years, considered an impossibility during peacetime!
John eventually got back into the cockpit in the B-52 and served numerous roles, including becoming a Wing Commander a few weeks after arriving on base when his wing failed an Operational Readiness Inspection (ORI) and the previous Wing Commander was fired. He instituted a corrective action program that resulted in his wing achieving the best bombing scores in the history of the Strategic Air Command during the ORI re-test.
Numerous other assignments, including another tour at the Pentagon, led to his selection as Lieutenant General (three-star). For most of these assignments, General Fairfield was not selected for these positions because of his in-depth knowledge of the intricacies of the tasks, but for his leadership and for his ability to inspire his men and women to achieve the goals of their mission.
General Fairfield retired from active duty in 1997.
Unmanned Aerial Systems (drones) pose a serious inflight risk to aircraft. In this episode, we discuss some of the findings in the comprehensive ASSURE study performed by 23 academic institutions.
After Otis Hooper graduated from the United States Air Force Academy, he attended Undergraduate Pilot Training in Columbus, MS, and then flew the KC-135 aircraft at McConnell Air Force Base in Kansas. He had just returned from his first deployment (of eight total) when the September 11th attacks occurred, and was assigned to fly refueling missions over New York City for the fighter aircraft protecting the city.
After leaving the active duty Air Force, he flew VIP airlift support missions in the C-40 Boeing Business Jet with the Washington, D.C. Air Guard. It was at this time that Otis started his fitness transformation. During an 18-month period, he dropped 50 pounds of fat, gained 25 pounds of muscle, and competed in the Mr. Olympia contest. He continues his bodybuilding activities, and has now become a professional.
But that's just the beginning of his non-flying activities. He trained for and completed an Ironman triathlon, and then competed on the American Ninja Warrior program. He is also a motivational speaker with the Afterburner Team, and has just started a career as a movie actor, appearing in Rampage with Dwayne Johnson.
- Pilots should avoid flight within areas of reported ongoing unauthorized laser activity to the extent practicable.
- In the event a cautionary broadcast (by ATC or another pilot) regarding unauthorized laser illumination is made within the previous 20 minutes for a particular area, pilots should avoid the area, if practicable.
- In the event laser activity is encountered or reported in the vicinity of flight, pilots operating in accordance with instrument flight rules (IFR) should obtain ATC authorization prior to deviating from their assigned clearance.
- In the event aircrews are unexpectedly exposed to laser illumination, direct eye contact with the beam should be avoided, and eyes should be shielded to the maximum extent possible consistent 4 with aircraft contract and safety. ATC understands that, under these circumstances, aircrews may regard the event as an in-flight emergency and may take evasive action to avoid further exposure to the laser illumination.
- As soon as possible, following an incident, pilots should report it to the appropriate ATC facility in accordance with the guidance provided by this AC. Forward as much information as available. Expeditious reporting will assist law enforcement in locating the source of the laser transmission.
This is our second visit with aviation artist and historian John Mollison. In this interview, John discusses his newest film, the award-winning South Dakota Warrior: The John Waldron Story.
On 4 June, 1942, LtCDR John C. Waldron led 29 other men into battle against the Japanese at the Battle of Midway. The result was (nearly) utter annihilation of his squadron...and the moment that assured that the United States would utterly defeat the Japanese. His mission led to the destruction of four Japanese aircraft carriers (the Soryu, the Hiryu, the Kaga and the Akagi) during the Battle of Midway, which changed the course of the war in the Pacific.
In Mollison's film, we learn the John Waldron story and the lessons of the Battle of Midway.
Turbulence is air movement that normally cannot be seen and often occurs unexpectedly. It can be created by many different conditions, including atmospheric pressure, jet streams, air around mountains, cold or warm weather fronts or thunderstorms. Turbulence can even occur when the sky appears to be clear.
While turbulence is normal and happens often, it can be dangerous. Its bumpy ride can cause passengers who are not wearing their seat belts to be thrown from their seats without warning. But, by following the guidelines suggested on this site, you can help keep yourself and your loved ones safe when traveling by air.
To keep you and your family as safe as possible during flight, FAA regulations require passengers to be seated with their seat belts fastened:
- When the airplane leaves the gate and as it climbs after take-off.
- During landing and taxi.
- Whenever the seat belt sign is illuminated during flight.
Why is it important to follow these safety regulations? Consider this:
- In nonfatal accidents, in-flight turbulence is the leading cause of injuries to airline passengers and flight attendants.
- Each year, approximately 58 people in the United States are injured by turbulence while not wearing their seat belts.
- From 1980 through 2008, U.S. air carriers had 234 turbulence accidents*, resulting in 298 serious injuries and three fatalities.
- Of the 298 serious injuries, 184 involved flight attendants and 114 involved passengers.
- At least two of the three fatalities involved passengers who were not wearing their seat belts while the seat belt sign was illuminated.
- Generally, two-thirds of turbulence-related accidents occur at or above 30,000 feet.
From Spencer Suderman's website:
Spencer Suderman is not only one of the most exciting air show performers on the planet, he is also a Guinness World Record holder! On March 20, 2016, Spencer flew the Sunbird S-1x, an experimental variant of the Pitts S-1 biplane to an altitude of 24,500′ in the restricted airspace over the Barry M. Goldwater Range in Yuma, Arizona then entered an inverted flat spin. At an altitude of 2,000′ the recovery was initiated and the Sunbird smoothly returned to level flight at 1,200′. A new world record of 98 inverted flat spins crushed the previous Guinness World Record of 81 that Spencer set in 2014.
Spencer began flying while in college in the late 1980’s and quickly advanced from private pilot to commercial pilot with an instrument rating. In 2002 he became a Certified Flight Instructor (CFI) and now holds an FAA unrestricted Statement of Aerobatic Competency (SAC) card allowing him to perform solo and formation aerobatics down to surface level.
While working on his instrument rating, Spencer discovered that aerobatics are amazingly fun and quickly lost interest in merely flying straight and level. After attending numerous aerobatic contests in the Super Decathlon aerobatic trainer rented from a local flight school he moved up to the high performance Pitts S-2B. He’s been performing in air shows since 2006 and the plane was dubbed the “Meteor Pitts” because it shoots across the sky with its unique hot rod style flame paint scheme.
Spencer’s air show performance uniquely showcases the capabilities of the Meteor Pitts Biplane with Intense gyroscopic maneuvers like the Double Hammerhead and the Inverted Flat Spin with its signature corkscrew smoke trail as the plane drops towards the ground at over 6000′ feet per minute spinning like a Frisbee!
Spencer enjoys entertaining the audience with this amazing airplane. His enthusiasm for flight is infectious and he’s proud of the people that have been motivated to get involved in aviation. Spencer enjoys producing videos about flying that give the viewer a sense of being in the cockpit going along for the ride!
When not flying Spencer works in IT within the entertainment industry and lives in Southern California with his wife, children, and two dogs. His educational background includes an MBA from the University of Massachusetts, Amherst and a bachelors degree from the State University of New York. Education is the most important pursuit any human can undertake and Spencer speaks from experience when encouraging young people to pursue learning with passion.
What is Precision Runway MonitorTraining?
Precision Runway Monitor (PRM) training provides guidance on conducting PRM approaches. These are simultaneous, independent approaches to closely spaced, parallel runways.
What You Need to Know
The FAA, together with industry, recently completed an extensive overhaul of the PRM training material. The centerpiece of this effort is a newly developed training aid titled, “Precision Runway Monitor (PRM) Pilot Procedures.” It replaces previously used training videos for both air carrier and general aviation pilots. Although the core elements of the training remain unchanged, this new version has been streamlined to reduce completion time and provides the most up-to-date information on how to safely conduct PRM approaches.
In conjunction with this change, the Aeronautical Information Manual (AIM) is being updated regarding simultaneous approaches in general, and PRM operations specifically. Over time, other relevant documents will also be updated.
To reduce cockpit workload, a new Attention All Users Page (AAUP) format will be implemented. This new format is shorter in length and delivers updated briefing material. It will be published on December 7, 2017.
The FAA’s PRM website (www.faa.gov/training_testing/training/prm)has been updated as well. Here, pilots can view or download the PRM training slide presentation. A link to the appropriate AIM section is also provided.
What Do I Need to Do?
Part 121, 129, and 135 operations:Pilots must comply with FAA-approved company training, as identified in their Operations Specifications.
Part 91 operations:Pilots operating transport category aircraft must be familiar with PRM and Simultaneous Offset Instrument Approaches (SOIA) operations as contained in the AIM. Training, at a minimum, must require pilots to view the new FAA slide presentation, "Precision Runway Monitor (PRM) Pilot Procedures."Pilots not operating transport category aircraft must be familiar with PRM and SOIA operations, as contained in the AIM. The FAA strongly recommends these pilots view the new FAA training slide presentation, "Precision Runway Monitor (PRM) Pilot Procedures."
Aviation was in Lynn Damron's blood from the time he was born. His uncle was a barnstormer in the 1930s and later became an airline pilot. Starting at about age 10, Lynn wanted to be a fighter pilot. He soloed a J-3 Cub when he as still in high school, and after a year at a civilian college he was accepted to the United States Air Force Academy, class of 1967. After graduation he attended Undergraduate Pilot Training (UPT) at Moody Air Force Base and was assigned to fly back-seat F-4s.
On the way to Vietnam his unit was diverted to Korea, and he spent six months there on an air defense assignment. After his F-4 assignment, Lynn went to Vietnam as a Forward Air Controller (FAC), based at Hue. After Vietnam he became an instructor pilot (IP) in the supersonic T-38 Talon, training UPT students. Following his IP assignment he became an F-105 Wild Weasel pilot at George Air Force Base, CA.
After an educational assignment at Air Command And Staff College Lynn was assigned to fly F-4s at Clark Air Base, Philippines. Following his final F-4 assignment Lynn served as a staff officer for his last eight years in the Air Force.
Lynn now serves in the Civil Air Patrol, mentoring cadets and flying search and rescue missions.
Concept of Operations
- Runway Status Lights is an essential FAA system which uses Airport Surface Survellance data to determine vehicle and aircraft locations. Runway Status Lights processes this data using complex software algorithms with adjustable parameters to control airfield lights in accordance with Air Traffic operations, including anticipated separation. Red airfield lights (Runway Entrance Lights and Takeoff Hold Lights) illuminate and extinguish as vehicles and aircraft traverse the airfield.
System
- Runway Status Lights integrates airport lighting equipment with approach and surface surveillance systems to provide a visual signal to pilots and vehicle operators indicating that it is unsafe to enter/cross or begin takeoff on runway. The system is fully automated based on inputs from surface and terminal surveillance systems. Airport surveillance sensor inputs are processed through light control logic that commands in-pavement lights to illuminate red when there is traffic on or approaching the runway.
- Runway Entrance Lights (RELs) provide signal to aircraft crossing entering runway from intersecting taxiway
- Takeoff Hold Lights (THLs) provide signal to aircraft in position for takeoff
-
Runway Entrance Lights
The Runway Entrance Lights system is composed of flush mounted, in-pavement, unidirectional fixtures that are parallel to and focused along the taxiway centerline and directed toward the pilot at the hold line. A specific array of Runway Entrance Lights lights include the first light at the hold line followed by a series of evenly spaced lights to the runway edge; and one additional light at the runway centerline in line with the last two lights before the runway edge (See FIG 2-1-9). When activated, these red lights indicate that there is high speed traffic on the runway or there is an aircraft on final approach within the activation area.
- Operating Characteristics – Departing Aircraft: When a departing aircraft reaches 30 knots, all taxiway intersections with Runway Entrance Lights arrays along the runway ahead of the aircraft will illuminate (see FIG 2-1-9). As the aircraft approaches a Runway Entrance Lights equipped taxiway intersection, the lights at that intersection extinguish approximately 2 to 3 seconds before the aircraft reaches it. This allows controllers to apply "anticipated separation" to permit Air Traffic Control to move traffic more expeditiously without compromising safety. After the aircraft is declared "airborne" by the system, all lights will extinguish.
- Operating Characteristics – Arriving Aircraft: When an aircraft on final approach is approximately 1 mile from the runway threshold all sets of Runway Entrance Light arrays along the runway will illuminate. The distance is adjustable and can be configured for specific operations at particular airports. Lights extinguish at each equipped taxiway intersection approximately 2 to 3 seconds before the aircraft reaches it to apply anticipated separation until the aircraft has slowed to approximately 80 knots (site adjustable parameter). Below 80 knots, all arrays that are not within 30 seconds of the aircraft's forward path are extinguished. Once the arriving aircraft slows to approximately 34 knots (site adjustable parameter), it is declared to be in a taxi state, and all lights extinguish.
- What a pilot would observe: A pilot at or approaching the hold line to a runway will observe Runway Entrance Lights illuminating and extinguishing in reaction to an aircraft or vehicle operating on the runway, or an arriving aircraft operating less than 1 mile from the runway threshold.
Whenever a pilot observes the red lights of the Runway Entrance Lights, that pilot will stop at the hold line, or along the taxiway path and remain stopped. The pilot will then contact Air Traffic Control for resolution if the clearance is in conflict with the lights. Should pilots note illuminated lights under circumstances when remaining clear of the runway is impractical for safety reasons (i.e., aircraft is already on the runway), the crew should proceed according to their best judgment while understanding the illuminated lights indicate the runway is unsafe to enter or cross. Contact Air Traffic Control at the earliest possible opportunity.

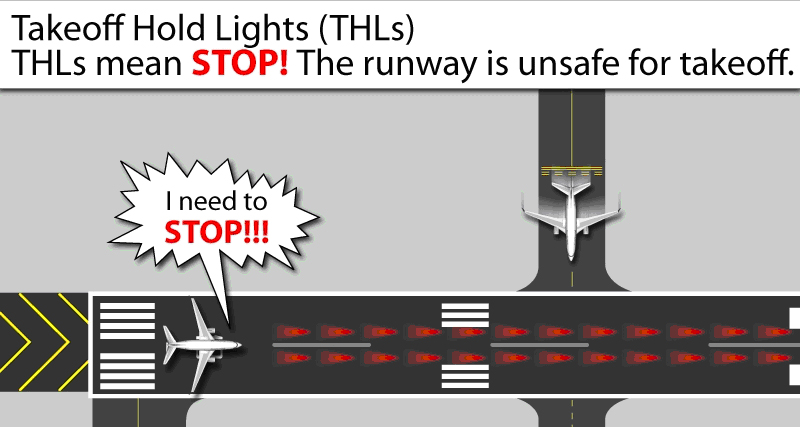
Takeoff Hold Lights
The Takeoff Hold Lights system is composed of in-pavement, unidirectional fixtures in a double longitudinal row aligned either side of the runway centerline lighting. Fixtures are focused toward the arrival end of the runway at the "line up and wait" point, and they extend for 1,500 feet in front of the holding aircraft (see FIG 2-1-9). Illuminated red lights provide a signal, to an aircraft in position for takeoff or rolling, that it is unsafe to takeoff because the runway is occupied or about to be occupied by another aircraft or ground vehicle. Two aircraft, or a surface vehicle and an aircraft, are required for the lights to illuminate. The departing aircraft must be in position for takeoff or beginning takeoff roll. Another aircraft or a surface vehicle must be on or about to cross the runway.
- Operating Characteristics – Departing Aircraft: Takeoff Hold Lights will illuminate for an aircraft in position for departure or departing when there is another aircraft or vehicle on the runway or about to enter the runway (see FIG 2-1-9.) Once that aircraft or vehicle exits the runway, the Takeoff Hold Lights extinguish. A pilot may notice lights extinguish prior to the downfield aircraft or vehicle being completely clear of the runway but still moving. Like Runway Entrance Lights, Takeoff Hold Lights have an "anticipated separation" feature.When the Takeoff Hold Lights extinguish, this is not clearance to begin a takeoff roll. All takeoff clearances will be issued by Air Traffic Control.
- What a pilot would observe: A pilot in position to depart from a runway, or has begun takeoff roll, will observe Takeoff Hold Lights illuminating in reaction to an aircraft or vehicle on the runway or about to enter or cross it. Lights will extinguish when the runway is clear. A pilot may observe several cycles of lights illuminating and extinguishing depending on the amount of crossing traffic.
- Whenever a pilot observes the red lights of the Takeoff Hold Lights, the pilot will stop or remain stopped. The pilot will contact Air Traffic Control for resolution if any clearance is in conflict with the lights. Should pilots note illuminated lights while in takeoff roll and under circumstances when stopping is impractical for safety reasons, the crew should proceed according to their best judgment while understanding the illuminated lights indicate that continuing the takeoff is unsafe. Contact Air Traffic Control at the earliest possible opportunity.
Pilot Actions
- When operating at airports with Runway Status Lights, pilots should turn the transponder "ON" with Altitude Enabled when operating on all taxiways and runways. This ensures interaction with the FAA surveillance systems which provide information to the Runway Status Lights system.
- Never cross over illuminated red lights. Under normal circumstances, Runway Status Lights will confirm the pilot's taxi or takeoff clearance. If Runway Status Lights indicates that it is unsafe to takeoff from or taxi across a runway, immediately notify Air Traffic Control of the conflict and confirm your clearance.
- Do not proceed when lights have extinguished without an Air Traffic Control clearance. Runway Status Lights verifies an Air Traffic Control clearance, it does not substitute for an Air Traffic Control clearance.
Air Traffic Control of Runway Status Lights
- Controllers can set in-pavement lights to one of five brightness levels to assure maximum conspicuity under all visibility and lighting conditions. Runway Entrance Lights and Takeoff Hold Lights subsystems may be independently set.
- The system can be shutdown should Runway Status Lights operations impact the efficient movement of air traffic or contribute, in the opinion of the Air Traffic Control Supervisor, to unsafe operations. Whenever the system is shutdown, a NOTAM must be issued, and the Automatic Terminal Information System must be updated.
Mark Berry started flying as a teenager, and attended Embry-Riddle Aeronautical University, earning all of his General Aviation (GA) ratings by the time he graduated. Following graduation, he paid his dues in GA, and passed his Airline Transport Pilot written exam and Practical Test (check ride), but couldn't receive his ATP rating until he turned 23 years old.
Flying Tigers Airline wanted to offer him employment, but couldn't hire him without an ATP. While he was waiting to "age" into his rating, he was hired by Trans World Airlines. His life was on track to a fantastic career, and he was engaged to his soul-mate, Suzanne.
Suzanne was traveling to Rome on business, seated in First Class of TWA Flight 800. When Flight 800 crashed, Mark's world fell apart. Every day he went to work he saw aircraft in his airline's livery that were identical to the plane that carried Suzanne to her death. Mark had to take time off, and had to find a way to deal with his loss.
In the long process of healing, Mark wrote two novels that explored survivor guilt. But he didn't deal with his own issues until, after much urging from family and publisher, he wrote his memoir, 13,700 Feet - My Personal Hole In The Sky.
Mark eventually recovered, and returned to airline flying. When TWA went out of business, he ended up at another airline, and is now a Captain.
Lightning has the potential to cause catastrophic damage to aircraft. It is estimated that lightning will strike an aircraft every 1000 flight hours, normally without serious complications. One of the more famous aircraft accidents caused by lightning was the 1963 crash of Pan Am flight 214, which crashed near the University of Delaware.
An immediate result of that crash was the requirement for all turbojet passenger aircraft to have lightning-dissipating static discharge wicks installed on the airplane wingtips. In addition, it was recommended that all jet aircraft use jet A fuel, rather than more volatile kerosene. Today, in the event of a lightning strike, the aluminum fuselage acts like a Faraday cage and diverts the thousands of amperes of electricity around the aircraft, not through it.
One day, while at Airventure at Oshkosh, Richard Taylor had a bold proposal to his friend, fellow pilot Pat Epps. "Let's fly over the magnetic north pole and do a roll to see what happens to the magnetic compass!" This was the start of a multi-attempt saga that took several years and took the pair on an adventure of a lifetime.
Richard Taylor had served in the U.S. Army as a paratrooper, then attended college. He had promised himself a Private Pilot certificate as a reward for finishing college, and that was the start of his aviation passion. In this podcast you will hear Richard recount his flight to the north pole, his authoring of the memoir Roll The Pole, and his project with Pat Epps to rescue the P-38 Glacier Girl from under 250 feet of ice.
From Wikipedia:
Jet lag, medically referred to as desynchronosis and rarely as circadian dysrhythmia, is a physiological condition which results from alterations to the body's circadian rhythms resulting from rapid long-distance trans-meridian (east–west or west–east) travel. For example, someone travelling from New York to London feels as if the time were five hours earlier than local time. Jet lag was previously classified as one of the circadian rhythm sleep disorders.
The condition of jet lag may last several days before the traveller is fully adjusted to the new time zone; a recovery period of one day per time zone crossed is a suggested guideline. Jet lag is especially an issue for airline pilots, crew, and frequent travellers. Airlines have regulations aimed at combating pilot fatigue caused by jet lag.
The term "jet lag" is used because before the arrival of passenger jet aircraft, it was uncommon to travel far and fast enough to cause desynchronosis. Travel by propeller-driven aircraft, by ship or by train was slower and of more limited distance than jet flights, and thus did not contribute widely to the problem.
The symptoms of jet lag can be quite varied, depending on the amount of time zone alteration, time of day, and individual differences. Sleep disturbance occurs, with poor sleep upon arrival and/or sleep disruptions such as trouble falling asleep (when flying east), early awakening (when flying west), and trouble remaining asleep. Cognitive effects include poorer performance on mental tasks and concentration; increased fatigue, headaches, and irritability; and problems with digestion, including indigestion, changes in the frequency of defecation and consistency of faeces, and reduced interest in and enjoyment of food. The symptoms are caused by a circadian rhythm that is out of sync with the day-night cycle of the destination, as well as the possibility of internal desynchronisation. Jet lag has been measured with simple analogue scales, but a study has shown that these are relatively blunt for assessing all the problems associated with jet lag. The Liverpool Jet Lag Questionnaire was developed to measure all the symptoms of jet lag at several times of day, and this dedicated measurement tool has been used to assess jet lag in athletes.
Jet lag may require a change of three time zones or more to occur, though some individuals can be affected by as little as a single time zone or the single-hour shift to or from daylight saving time. Symptoms and consequences of jet lag can be a significant concern for athletes traveling east or west to competitions, as performance is often dependent on a combination of physical and mental characteristics that are impacted by jet lag.
Travel fatigue is general fatigue, disorientation, and headache caused by a disruption in routine, time spent in a cramped space with little chance to move around, a low-oxygen environment, and dehydration caused by dry air and limited food and drink. It does not necessarily involve the shift in circadian rhythms that cause jet lag. Travel fatigue can occur without crossing time zones, and it often disappears after a single day accompanied by a night of good quality sleep.
Jet lag is a chronobiological problem, similar to issues often induced by shift work and the circadian rhythm sleep disorders. When traveling across a number of time zones, the body clock (circadian rhythm) will be out of synchronization with the destination time, as it experiences daylight and darkness contrary to the rhythms to which it has grown accustomed. The body's natural pattern is upset, as the rhythms that dictate times for eating, sleeping, hormone regulation, body temperature variations, and other functions no longer correspond to the environment, nor to each other in some cases. To the degree that the body cannot immediately realign these rhythms, it is jet lagged.
The speed at which the body adjusts to the new schedule depends on the individual as well as the direction of travel; some people may require several days to adjust to a new time zone, while others experience little disruption.
Crossing the International Date Line does not in itself contribute to jet lag, as the guide for calculating jet lag is the number of time zones crossed, with a maximum possible time difference of plus or minus 12 hours. If the time difference between two locations is greater than 12 hours, one must subtract that number from 24. For example, the time zone UTC+14 will be at the same time of day as UTC−10, though the former is one day ahead of the latter.
Jet lag is linked only to the trans-meridian (west–east or east–west) distance travelled. A ten-hour flight between Europe and southern Africa does not cause jet lag, as the direction of travel is primarily north–south. A five-hour flight between the Pacific and Atlantic coasts of the United States may well result in jet lag.
There are two separate processes related to biological timing: circadian oscillators and homeostasis. The circadian system is located in the suprachiasmatic nucleus (SCN) in the hypothalamus of the brain. The other process is homeostatic sleep propensity, which is a function of the amount of time elapsed since the last adequate sleep episode.
The human body has a master clock in the SCN and also peripheral oscillators in tissues. The SCN's role is to send signals to peripheral oscillators, which synchronise them for physiological functions. The SCN responds to light information sent from the retina. It is hypothesised that peripheral oscillators respond to internal signals such as hormones, food intake, and "nervous stimuli"
The implication of independent internal clocks may explain some of the symptoms of jet lag. People who travel across several time zones can, within a few days, adapt their sleep-wake cycles with light from the environment. However, their skeletal muscles, liver, lungs and other organs will adapt at different rates.This internal biological de-synchronization is exacerbated as the body is not in sync with the environment—a "double desynchronization", which has implications for health and mood.
Raymond Leopold knew he wanted to be a pilot since he was a child. He took flying lessons before entering the United States Air Force Academy, and continued his lessons with the Academy Aero Club. After graduation, he went to graduate school, earning his Master's Degree in Electrical Engineering, before attending Air Force Undergraduate Pilot Training.
In pilot training, he was at the top of his class. In fact, to celebrate the fact that he was the first student to solo in a jet, his classmates threw him into the swimming pool. In the process, he was injured, herniating three lumbar discs, and was medically eliminated from pilot training.
The Air Force assigned him to a position that would let him utilize his education, and he attended night classes to pursue his Doctorate in Electrical Engineering. He followed this assignment with a stint teaching at the Air Force Academy. By this time he had become a CFI, and was selected to supervise the Balloon Club at the Academy, earning his balloon ratings in the process.
Ray's career included a tour at the Pentagon, working with aviation pioneer John Boyd. After serving twenty years in the Air Force, Ray made the hard choice to pursue a civilian career. And that's where he changed the world.
Ray was hired by Motorola, and created the satellite telephone system that became known as Iridium. In this podcast, you'll hear a recap of the incredible efforts that went into launching 77 communications satellites and the system that now enables telephone calls from anywhere on the planet.
You'll also hear about how Ross Perot was willing to bankroll Ray in his attempt to lead the first team to successfully fly across the Atlantic Ocean in a balloon.
Drug testing is a way of life for pilots and other transportation workers. As a pilot, you will receive pre-employment drug testing, random (no-notice) drug testing, and reasonable-cause drug testing throughout your career.
Gateway Select is an innovative talent pathway for those seeking to become pilots at JetBlue. This particular Gateway Program will allow an applicant, if successful, to learn with us from the beginning and become a JetBlue pilot after completing a rigorous training program.
This unique, accessible and cost effective JetBlue Pilot Gateway Program will take a more competency-based approach to becoming a professional pilot. The Program will optimize the training of prospective airline pilots by offering early exposure to multi-crew/multi-engine operations, full motion simulator training, crew resource management, and threat and error management. Once meeting all program requirements, including the FAA's 1,500 flight-hour requirement, pilots will become a new hire at JetBlue. At that time, graduates will go through the same orientation and six-week instruction that all E190 first officers complete.